-
Show with sketches how to combine
- two identical capacitors to give an equivalent capacitance half as big as either; 1
- two identical resistors to give an equivalent resistance half as big as either; 2
- two identical coils to give an equivalent inductance half as big as either; 3
- two identical batteries to give an equivalent voltage half as big as either. 4
-
Explain why a static magnetic field can't change
the kinetic energy of a charged particle.
5
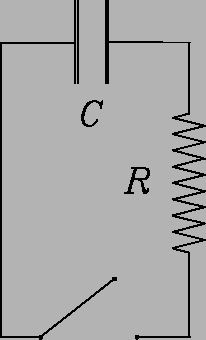
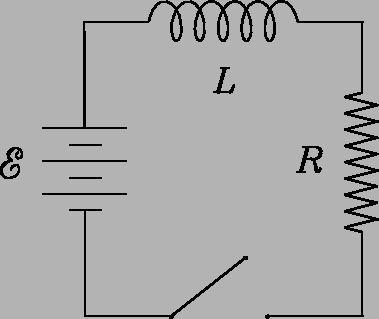
Describe in quantitative detail what happens after the switch is closed at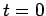 in each of the following circuits, where
in each of the following circuits, where
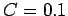 F,
F,
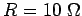 ,
, 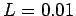 H and
H and 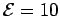 V.
V.
(Graphs are fine as long as the axes are labeled quantitatively.) -
The capacitor is initially charged to
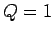 C:
6
C:
6
-
7
-
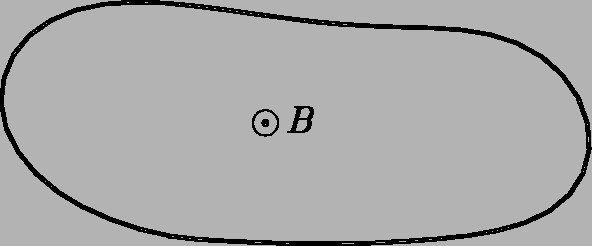
A loop of limp braided wire lies flat on a frictionless table
in an elongated oval shape.
Suddenly a uniform magnetic field is turned on
normal to the table's surface.
What happens to the loop? Why?
8
An idealized coaxial cable consists of a solid cylindrical wire
of length ![]() and radius
and radius ![]() coated with a thin layer of insulating paint
and a second thin layer of metal (outside the paint, so that
it does not make electrical contact with the inner wire).
The thickness of the paint and that of the outer conductor
are both negligible compared with
coated with a thin layer of insulating paint
and a second thin layer of metal (outside the paint, so that
it does not make electrical contact with the inner wire).
The thickness of the paint and that of the outer conductor
are both negligible compared with ![]() ,
and we shall treat the wire as "long" (
,
and we shall treat the wire as "long" (![]() )
so that "end effects" can be neglected.
)
so that "end effects" can be neglected.
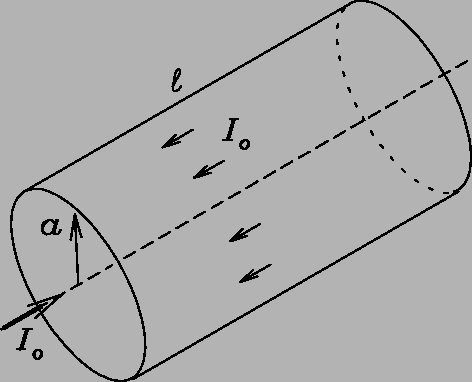
A net current ![]() flows down the solid central conductor
and back (in the opposite direction) along the thin outer conductor.
The current density
flows down the solid central conductor
and back (in the opposite direction) along the thin outer conductor.
The current density
![]() is uniform over
the cross-sectional area of the central conductor and
the returning current is uniformly distributed
over the surface of the outer conducting shell.
is uniform over
the cross-sectional area of the central conductor and
the returning current is uniformly distributed
over the surface of the outer conducting shell.
- [10 marks]
In what direction is the vector magnetic field
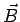 inside and outside the cable?
(Indicate on the sketch and/or in words.)
9
inside and outside the cable?
(Indicate on the sketch and/or in words.)
9
- [10 marks]
Calculate the magnetic field strength
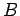 as a function of
as a function of 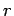 (the distance from the central axis),
(the distance from the central axis),
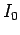 ,
, 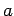 and any fundamental constants,
both inside and outside the cable.
10
and any fundamental constants,
both inside and outside the cable.
10
- [10 marks]
Calculate the cable's inductance in terms of
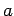 and
and 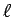 .
11
.
11
- [10 marks]
Describe what would happen in the cable
if the battery driving the current
were suddenly "shorted out" by a superconducting switch. 12 - Now assume that the thin outer conductor has no resistance
but the solid inner conductor has a resistivity
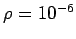
 m. If
m. If 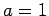 mm and
mm and 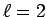 m,
what is the resistance of the cable?
13
m,
what is the resistance of the cable?
13
- [5 marks] If
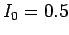 A, what is the
electric field
A, what is the
electric field
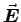 in the inner conductor?
14
in the inner conductor?
14