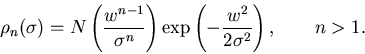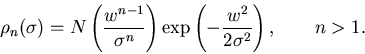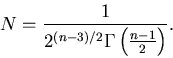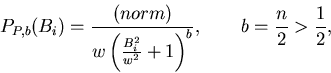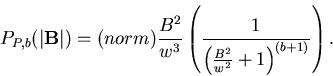

Next: A different way to go from Gaussian toward
Up: Between Gaussian and Lorentzian
Previous: Between Gaussian and Lorentzian
Consider changing
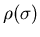 ,
the distribution of classes, to
,
the distribution of classes, to
The normalization N is
Convolution of this with the Gaussian distribution produces Pearson
distributions[2]
This includes the Lorentzian as the b=1 special case, and the Gaussian as
the
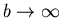 limit. While it is thus expected that the
relaxation function
GP,b(t) will evolve smoothly from Lorentzian KT to
Gaussian KT as b increases, b=2 (n=4) is the only nontrivial case for
which closed form G(t) is known:
limit. While it is thus expected that the
relaxation function
GP,b(t) will evolve smoothly from Lorentzian KT to
Gaussian KT as b increases, b=2 (n=4) is the only nontrivial case for
which closed form G(t) is known:
Jess H. Brewer
2002-09-24